Azure Apps: 7 Ultimate Power Tips for Dominating Cloud Development
Welcome to the future of cloud-powered applications. In this deep dive, we explore everything you need to know about Azure apps—your gateway to scalable, secure, and lightning-fast cloud solutions.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Azure apps refer to applications built, deployed, and managed using Microsoft Azure’s cloud platform. These aren’t just websites or mobile backends—they’re full-stack, cloud-native solutions that leverage the power of global data centers, AI integrations, and enterprise-grade security. Whether you’re building a simple web app or a complex microservices architecture, Azure apps provide the infrastructure and tools to make it happen.
Defining Azure Apps in Modern Development
Azure apps encompass a broad range of services under the Microsoft Azure umbrella, including App Services, Functions, Logic Apps, and Container Instances. These services allow developers to deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure—a hallmark of Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). This abstraction enables faster development cycles and reduced operational overhead.
- Azure App Service for web and mobile apps
- Azure Functions for serverless computing
- Azure Logic Apps for workflow automation
Each of these components plays a vital role in shaping how modern applications are built and scaled. For instance, Azure App Service supports multiple languages like .NET, Java, Node.js, and Python, making it highly versatile for diverse development teams.
Evolution from On-Premise to Cloud-Native Apps
The shift from traditional on-premise software to cloud-native Azure apps has been revolutionary. Organizations no longer need to invest in physical servers or maintain complex networking setups. Instead, they can spin up environments in minutes, scale dynamically based on traffic, and pay only for what they use.
“Cloud computing is not just a technology shift—it’s a business transformation.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
This transition has empowered startups and enterprises alike to innovate faster. With Azure apps, companies can deploy globally in seconds, integrate AI models via Azure Cognitive Services, and ensure compliance with industry standards like HIPAA and GDPR.
Core Components of Azure Apps Ecosystem
Understanding the building blocks of Azure apps is essential for leveraging the platform effectively. Microsoft has designed a modular ecosystem where each service complements the other, enabling seamless integration and deployment workflows.
Azure App Service: The Heart of Web Applications
Azure App Service is arguably the most widely used component when discussing Azure apps. It allows developers to host web apps, REST APIs, and mobile backends with built-in support for continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD).
- Supports Windows and Linux environments
- Integrated with GitHub, Azure DevOps, and Bitbucket
- Auto-scaling and load balancing capabilities
One of the standout features is its ability to run in different pricing tiers—from free shared instances to isolated Premium V3 plans suitable for enterprise workloads. This flexibility makes Azure App Service ideal for both prototyping and production-grade deployments.
For more details, visit the official Azure App Service page.
Azure Functions: Serverless Computing Made Simple
Serverless computing has gained massive traction, and Azure Functions is Microsoft’s answer to AWS Lambda. With Azure Functions, you can run small pieces of code (functions) in response to events—like HTTP requests, database changes, or file uploads—without provisioning or managing servers.
- Event-driven execution model
- Pay-per-execution pricing
- Supports multiple languages including C#, JavaScript, Python, and PowerShell
This makes Azure Functions perfect for microservices, background processing, and real-time data pipelines. For example, an e-commerce platform might use Azure Functions to send confirmation emails after a purchase, resize product images upon upload, or trigger fraud detection algorithms.
Azure Logic Apps: Automating Business Workflows
While Azure Functions handle code-level automation, Azure Logic Apps focus on high-level workflow orchestration. These are visual tools that let you connect disparate systems—like Salesforce, Office 365, SAP, or Twitter—using pre-built connectors.
- Drag-and-drop workflow designer
- Over 500+ built-in connectors
- Integration with Azure API Management and Service Bus
For instance, a marketing team could automate lead capture by setting up a Logic App that triggers when a new form submission arrives in SharePoint, then creates a contact in Dynamics 365 and sends a welcome email via SendGrid—all without writing a single line of code.
Benefits of Using Azure Apps for Enterprise Solutions
Enterprises are increasingly adopting Azure apps due to their scalability, security, and integration capabilities. Let’s explore the key advantages that make Azure a top choice for large-scale application development.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
One of the most compelling reasons to use Azure apps is their ability to scale automatically. Whether you’re experiencing a sudden spike in user traffic or planning for seasonal demand, Azure’s auto-scaling features ensure your applications remain responsive.
- Vertical and horizontal scaling options
- Integration with Azure Monitor for performance tracking
- Content delivery via Azure CDN
Azure App Service, for example, allows you to configure scaling rules based on CPU usage, memory consumption, or queue length. You can also use Azure Monitor to set up alerts and analyze logs in real time, ensuring optimal performance at all times.
Enterprise-Grade Security and Compliance
Security is non-negotiable for enterprise applications, and Azure apps deliver robust protection out of the box. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity and operates one of the most secure cloud infrastructures in the world.
- Built-in DDoS protection
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Encryption at rest and in transit
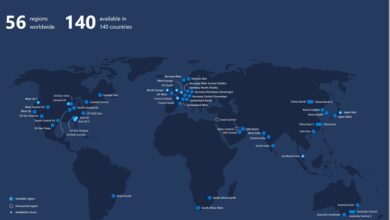
Azure also complies with over 140 international and industry-specific standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2, HIPAA, and GDPR. This makes it easier for organizations in healthcare, finance, and government sectors to meet regulatory requirements when deploying Azure apps.
“Security is not a feature—it’s a foundation.” — Microsoft Azure Trust Center
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
Unlike traditional IT models that require upfront capital investment, Azure apps operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model. This means you only pay for the resources you consume, which can lead to significant cost savings.
- No long-term contracts or upfront fees
- Free tier available for learning and testing
- Reserved instances for predictable workloads
Additionally, Azure offers cost management tools like Azure Cost Management + Billing, which help track spending, set budgets, and identify underutilized resources. This transparency empowers teams to optimize cloud usage and avoid unexpected charges.
How to Build Your First Azure App: Step-by-Step Guide
Getting started with Azure apps doesn’t require years of experience. With the right guidance, you can deploy your first application in under 30 minutes. Here’s a practical walkthrough.
Setting Up Your Azure Account and Portal Access
The first step is creating a Microsoft Azure account. You can sign up for a free trial that includes $200 in credits and access to most services for 30 days.
- Visit Azure Free Account page
- Sign in with your Microsoft account or create a new one
- Verify your identity with a credit card (no charge unless you upgrade)
Once registered, you’ll gain access to the Azure Portal—a web-based interface where you can manage all your cloud resources. The portal is intuitive, featuring dashboards, resource groups, and quick-start templates to accelerate development.
Creating a Web App Using Azure App Service
Now, let’s deploy a simple web application using Azure App Service.
- In the Azure Portal, click Create a resource
- Search for App Service and select it
- Click Create
- Fill in the required details: Subscription, Resource Group, Name (e.g., my-first-azure-app)
- Choose Runtime Stack (e.g., .NET 6)
- Select Region (preferably closest to your users)
- Choose Pricing Tier (start with Free F1 for testing)
- Click Review + Create, then Create
After deployment (usually within 2-3 minutes), navigate to the resource and copy the URL. Your app is now live on the internet! You can later connect it to a custom domain, enable HTTPS, or link it to a GitHub repository for automated deployments.
Deploying Code via GitHub Integration
To automate deployments, integrate your Azure app with GitHub.
- In the App Service menu, go to Deployment Center
- Select GitHub as the source
- Authorize Azure to access your GitHub account
- Choose your repository and branch
- Click Finish
Now, every time you push code to your selected branch, Azure will automatically rebuild and redeploy your application. This CI/CD pipeline ensures that updates are seamless and reduces manual errors.
Advanced Features of Azure Apps for Developers
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to explore advanced capabilities that elevate your Azure apps to the next level.
Using Azure DevOps for CI/CD Pipelines
Azure DevOps is a powerful suite that integrates seamlessly with Azure apps to provide end-to-end DevOps workflows. From version control (Azure Repos) to automated testing (Azure Test Plans), it streamlines the entire software development lifecycle.
- Create YAML-based pipelines for consistent builds
- Run unit tests and integration tests in the cloud
- Deploy to multiple environments (dev, staging, production)
For example, you can set up a pipeline that triggers on every pull request, runs automated tests, and deploys to a staging environment only if all checks pass. This ensures code quality and reduces the risk of introducing bugs into production.
Learn more at Azure DevOps Documentation.
Integrating AI and Machine Learning Models
Azure apps can be supercharged with artificial intelligence using Azure Cognitive Services and Azure Machine Learning. These tools allow developers to embed vision, speech, language, and decision-making capabilities into their applications.
- Use Computer Vision API to analyze images
- Implement Text Analytics for sentiment analysis
- Train custom ML models using Azure ML Studio
Imagine a customer support chatbot built on Azure Functions that uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand user queries and route them to the appropriate department. Or a mobile app that leverages Face API to authenticate users securely. These scenarios are not futuristic—they’re achievable today with Azure apps.
Monitoring and Diagnostics with Application Insights
Even the best applications can face performance issues. That’s where Azure Application Insights comes in—a powerful monitoring tool that provides real-time insights into your app’s health.
- Track requests, exceptions, and dependencies
- Monitor custom metrics and logs
- Set up smart alerts for anomalies
Application Insights is part of Azure Monitor and can be enabled with just a few clicks in the Azure Portal. It helps developers identify bottlenecks, debug errors, and optimize user experience by analyzing telemetry data.
“You can’t improve what you can’t measure.” — W. Edwards Deming
Scaling Azure Apps for High-Traffic Scenarios
As your application grows, so does the demand on your infrastructure. Azure apps are designed to scale, but doing it right requires strategy and planning.
Auto-Scaling Based on Demand
Azure App Service allows you to configure auto-scaling rules that respond to metrics like CPU usage, memory, or HTTP queue length. For example, you can set a rule to add more instances when CPU exceeds 70% for five minutes.
- Scale out (add instances) during peak hours
- Scale in (reduce instances) during low traffic
- Use predictive scaling for scheduled events
This dynamic scaling ensures high availability while keeping costs under control. You can also use Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for containerized applications that require even greater scalability and orchestration.
Using Azure CDN for Global Content Delivery
Latency is a major factor in user experience. To deliver content faster to users around the world, Azure offers Content Delivery Network (CDN), which caches static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript files at edge locations.
- Reduce load times by serving content from nearby nodes
- Improve SEO rankings with faster page loads
- Support HTTPS and custom domains
By integrating Azure CDN with your Azure app, you ensure that users in Tokyo, London, or New York get the same fast experience as those in your home region.
Explore Azure CDN documentation for setup guides.
Database Scaling with Azure SQL and Cosmos DB
Your app is only as fast as its database. Azure provides two powerful options: Azure SQL Database for relational data and Azure Cosmos DB for globally distributed, NoSQL workloads.
- Azure SQL supports auto-tuning and elastic pools
- Cosmos DB offers single-digit millisecond latency at the 99th percentile
- Both support automatic backups and geo-replication
For high-traffic applications, Cosmos DB is particularly effective due to its multi-region replication and guaranteed SLAs. You can configure it to replicate data across continents, ensuring resilience and low latency for global users.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite its advantages, working with Azure apps can present challenges, especially for beginners. Let’s address some common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
Managing Costs Without Overspending
One of the biggest concerns with cloud platforms is unexpected billing. While Azure offers pay-as-you-go pricing, misconfigured resources can lead to high costs.
- Use Azure Cost Management to set budgets and alerts
- Delete unused resources (e.g., old test apps)
- Choose the right pricing tier—don’t over-provision
Regularly review your spending dashboard and tag resources by project or department to track accountability. This proactive approach prevents bill shock and ensures financial control.
Debugging Deployment Failures
Deployment issues are common, especially when integrating with third-party services or using complex configurations.
- Check deployment logs in the Azure Portal
- Use Kudu console for App Service debugging
- Validate connection strings and environment variables
If your app fails to start, enable Application Logging and Web Server Logging to capture detailed error messages. Often, the issue lies in missing dependencies or incorrect runtime settings.
Ensuring High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Downtime can be costly. To ensure your Azure apps remain available, implement redundancy and backup strategies.
- Deploy across multiple regions using Traffic Manager
- Enable geo-redundant storage for backups
- Test failover procedures regularly
Azure Site Recovery can automate disaster recovery for virtual machines, while Azure Backup provides scheduled snapshots of your apps and databases. These tools are essential for maintaining business continuity.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps are applications developed and hosted on Microsoft Azure’s cloud platform. They include web apps, mobile backends, serverless functions, and automated workflows built using services like Azure App Service, Functions, and Logic Apps.
How much does it cost to run an Azure app?
Costs vary based on usage. Azure offers a free tier for testing, and most services follow a pay-as-you-go model. For example, Azure App Service starts at $0/month for the Free tier, while premium plans can range from $70 to thousands per month depending on scale.
Can I deploy a custom domain to my Azure app?
Yes. You can map a custom domain (e.g., yourcompany.com) to your Azure app through the Azure Portal. You’ll need to verify domain ownership and configure DNS settings with your registrar.
Is Azure better than AWS for app development?
Both platforms are powerful, but Azure excels in integration with Microsoft products (like Office 365 and Active Directory), hybrid cloud scenarios, and enterprise support. The choice depends on your tech stack and business needs.
How do I secure my Azure app?
Use Azure’s built-in security features: enable HTTPS, configure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), use Azure Firewall, and integrate with Azure Active Directory for authentication. Regularly apply security updates and monitor logs.
Mastering Azure apps opens the door to scalable, secure, and intelligent cloud applications. From simple websites to AI-powered enterprise systems, Microsoft Azure provides the tools, infrastructure, and ecosystem to bring your ideas to life. By understanding its core components, leveraging automation, and planning for growth, you can build applications that are not only powerful but future-ready. Whether you’re a solo developer or part of a large team, Azure apps offer a robust foundation for innovation in the digital age.
Further Reading: